Amorepacific R&D Center Green Tea Probiotics Research Center identified skin anti-inflammatory effects of the exosomes found in green tea probiotics. The study was published on the online edition (Volume 9) of the internationally renowned journal in the field, Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, on July 17. (Paper Title: Lactobacillus plantarum-derived extracellular vesicles induce anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage polarization in vitro)
Since its establishment in February this year, Amorepacific R&D Center Green Tea Probiotics Research Center continues to study and identify the effects of Lactobacillus plantarum APsulloc 331261, a new plant-based green tea probiotics found exclusively in the organic tea fields of Jeju. Also, it is expanding the scope of the research to include microbiome or microorganisms living in the human body and their genetic information. The research center discovered that the green tea probiotics has outstanding effects on the gastrointestinal tract compared to existing probiotics. And now, the center published its findings on having identified anti-inflammatory effects of green tea probiotics-derived exosomes on skin tissues and immune cells.
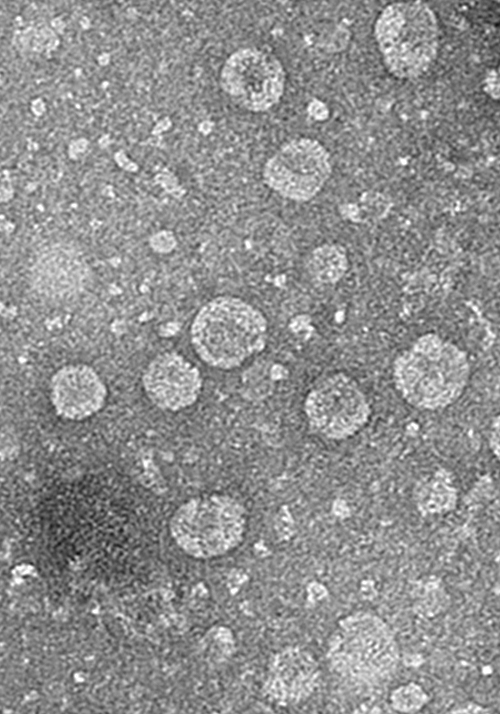
Exosomes (extracellular vesicles) are nanosized (around 100 nm) natural nanoparticles evolutionarily preserved and secreted to deliver information between cells. Exosomes are bio-friendly transporters that can quickly and accurately signal substances to other living organisms or cells, recently gaining much attention in the areas of life science and medicine globally.
Amorepacific R&D Center Chief Researcher Cho Eun-gyung and Research Group extracted and refined the exosomes from the plant-derived green tea probiotics exclusively found in the organic green tea fields of Jeju. They found that the exosomes defined the width and depth of the inflammatory response of undifferentiated monocyte and that they induce division to Type II macrophage 2b (M2b), which leads anti-inflammatory effect. The study also confirmed that green tea probiotics exosomes improve skin’s excessive inflammation, demonstrating anti-inflammatory effect.
Head of Amorepacific R&D Center Park Young-ho said, “The paper published by Green Tea Probiotics Research Center has significance in that it discovered the effect of exosome, which receives attention from academia in life science across the world, on skin and its potential for application” and added his commitment saying, “Amorepacific R&D Center is dedicated to continue to further study probiotics, the key to controlling microbiome, and exosome, the core of probiotics, to deliver innovative skin solutions to customers worldwide.”
Since 2013, Amorepacific R&D Center has published the results of its research on the function of skin cell exosomes, effects and mechanisms of exosomes that cause acne and atopy and continues to study the skin ecosystem centered around exosomes.